A recent study from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has identified a set of molecular biomarkers that can be used in the differential diagnosis of acute bacterial and viral infections. These biomarkers are different messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules found in the blood; differences in their levels can detect and predict with high probability if an infection is viral or bacterial.
The current COVID-19 pandemic is a grim testimony to the damage an infectious disease can cause to human health and welfare. A major challenge in treating such diseases is misdiagnosis, which can lead to trial-and-error treatments, and improper use of antibiotics. Identifying the correct type of infection is therefore critical, say IISc statement.
The human body responds to bacterial and viral infections differently. It produces different types of molecules ‒ such as proteins and RNA ‒ in the blood, depending on the type of infection. While antibiotics can treat bacterial infections, they are ineffective against viral infections. However, indiscriminate use of antibiotics to treat any kind of infection has given rise to bacterial strains that are now resistant to our entire arsenal of antibiotics. “Antibiotics are given even for viral infections in some cases because of misdiagnosis. With current methods, it can take a lot of time to test for bacterial or viral infections,” explains first author Sathyabaarathi Ravichandran, Research Associate in the lab of Nagasuma Chandra, Professor at the Department of Biochemistry.
A quick method to detect acute viral and bacterial infections and distinguish between them can be immensely useful in the clinic, as accurate diagnosis will win half the battle and guide the clinician towards the optimal treatment path. It will also prevent the rise of such antimicrobial resistance. In the new study, published in the journal EBioMedicine, the researchers have developed such a test using patient blood transcriptomes and sophisticated computational modelling.
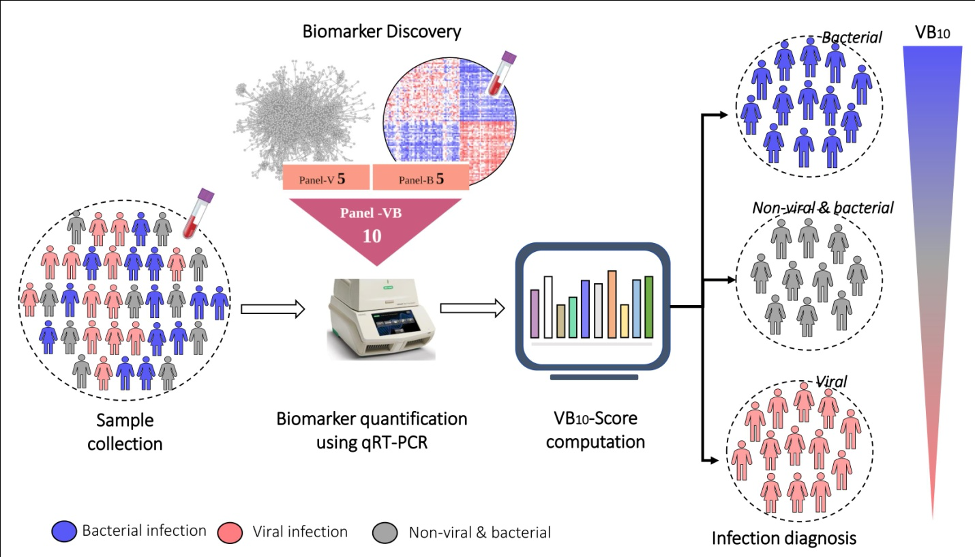
A transcriptome is a full set of mRNA molecules expressed by a biological cell, which is measured using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies. During an infection, there are specific genes that get turned on and these in turn lead to higher amounts of specific mRNAs and ultimately higher amounts of the corresponding proteins. The scientists analysed transcriptomic data of patients (from publicly available databases, and samples collected from MS Ramaiah Medical College in collaboration with a clinical team) and discovered a ten-gene RNA signature in the patients’ blood that is produced in varying quantities for viral and bacterial infections.
To make it useful in the clinic, the researchers devised a standalone score called VB10, which could be used for diagnosis, monitoring the stage of recovery after infection, and estimating the severity of the infection. VB10 accurately indicated whether a given blood sample had a bacterial or viral infection, across different bacteria and viruses and across different age groups.
The authors suggest that the test could be useful for differentiating COVID-19 infection from bacterial infections as well. In the study, they looked at various viral infections for which transcriptomic data is publicly available. This allowed them to develop a generic VB10 test score for viral infections. As soon as transcriptomic data became available for COVID-19, the team tested their approach and found that the test scores could differentiate between SARS-CoV-2 infection and common bacterial respiratory infections.
This work was done in collaboration with clinicians at MS Ramaiah Medical College and researchers Amit Singh, Dipshikha Chakravortty and KN Balaji at IISc. The team hopes to begin a trial study to translate their research from the lab to the clinic. “This test can be done using qRT-PCR. Given how common RT-PCR has become due to the pandemic, getting this test off the ground should not pose a major challenge,” says Chandra. The researchers expect it to be useful early on during the infection, and work against any strain. This can supplement the current COVID-19 diagnosis tests. (India Science Wire)

















Discussion about this post